What’s in a WINDOW?
Post-Occupancy Survey of a Study
To identify if the intended comfort and health parameters determined during design are met through an elaborate post-occupancy survey.
Study Questions
•To determine if the design of the window provides the intended light and heat control.
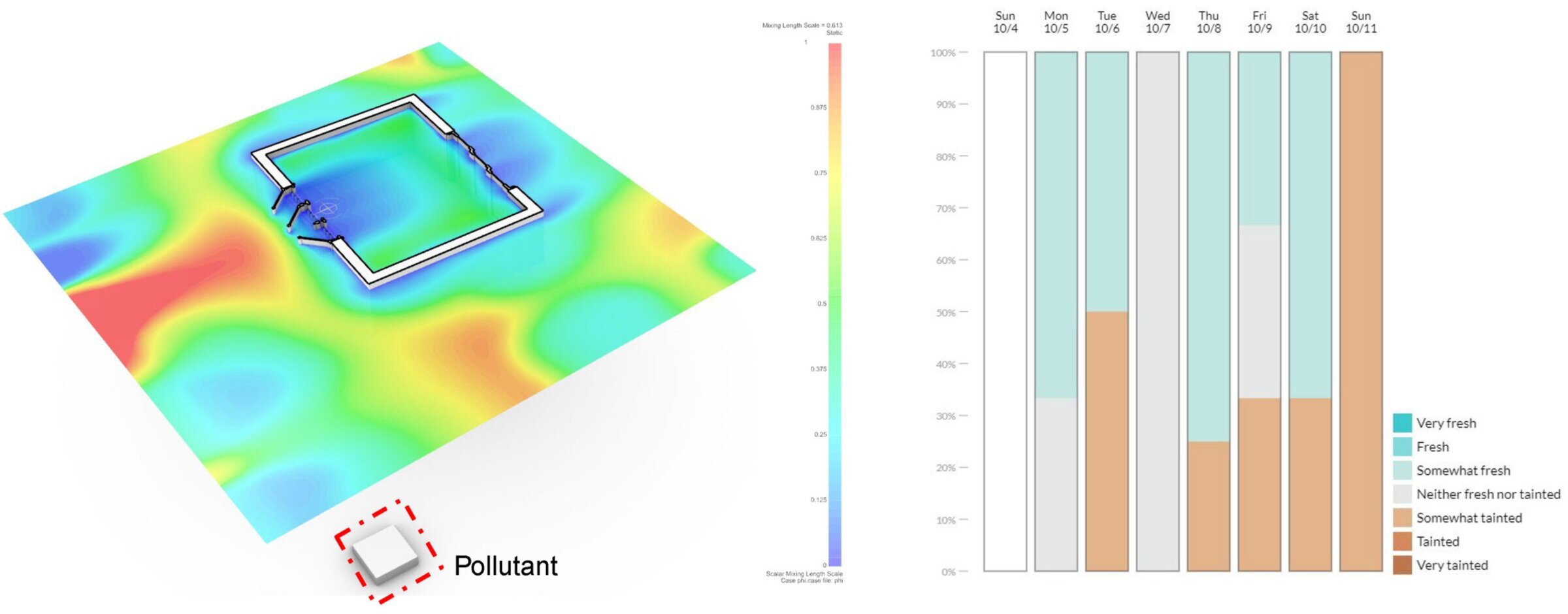
•To determine how much of the exterior conditions and activity are influencing the micro-climate.
•To determine the comfort of the user and the occupancy rate.
Location: Chennai, India
Climate: Tropical – Hot and Humid
Ambient Temperature: 91°F
Relative Humidity: 60%
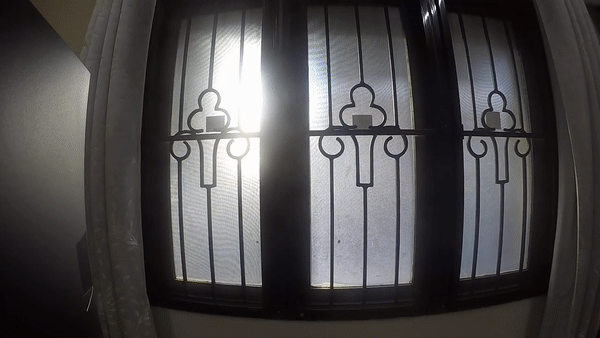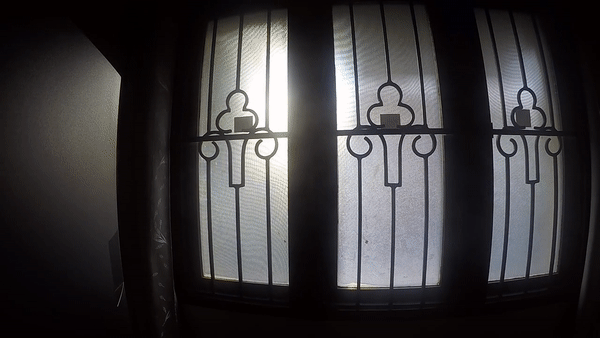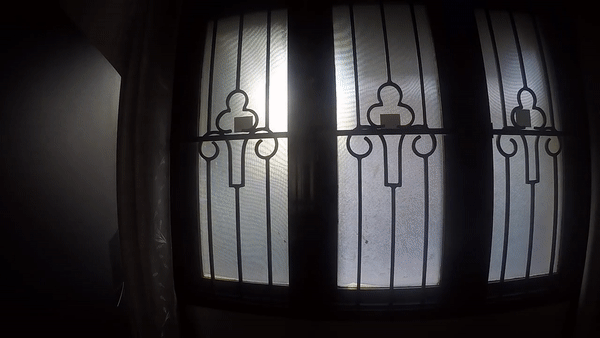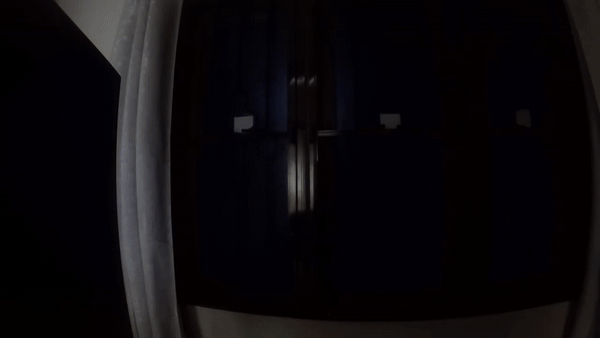
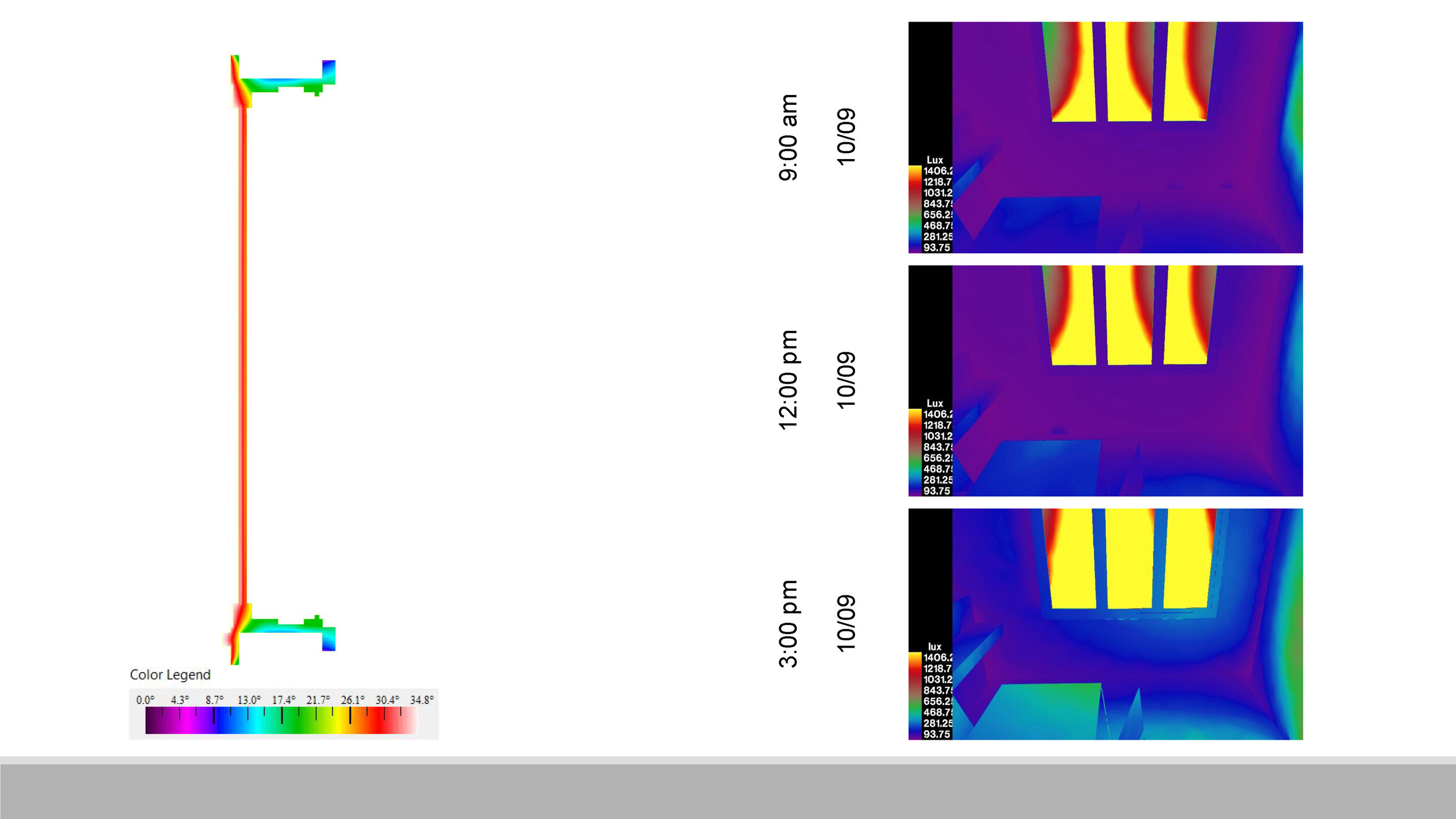
DAYLIGHT AND GLARE
OPEN
DAY - NOON
CLOSED
DAY - NOON
NOON - NIGHT
NOON - NIGHT
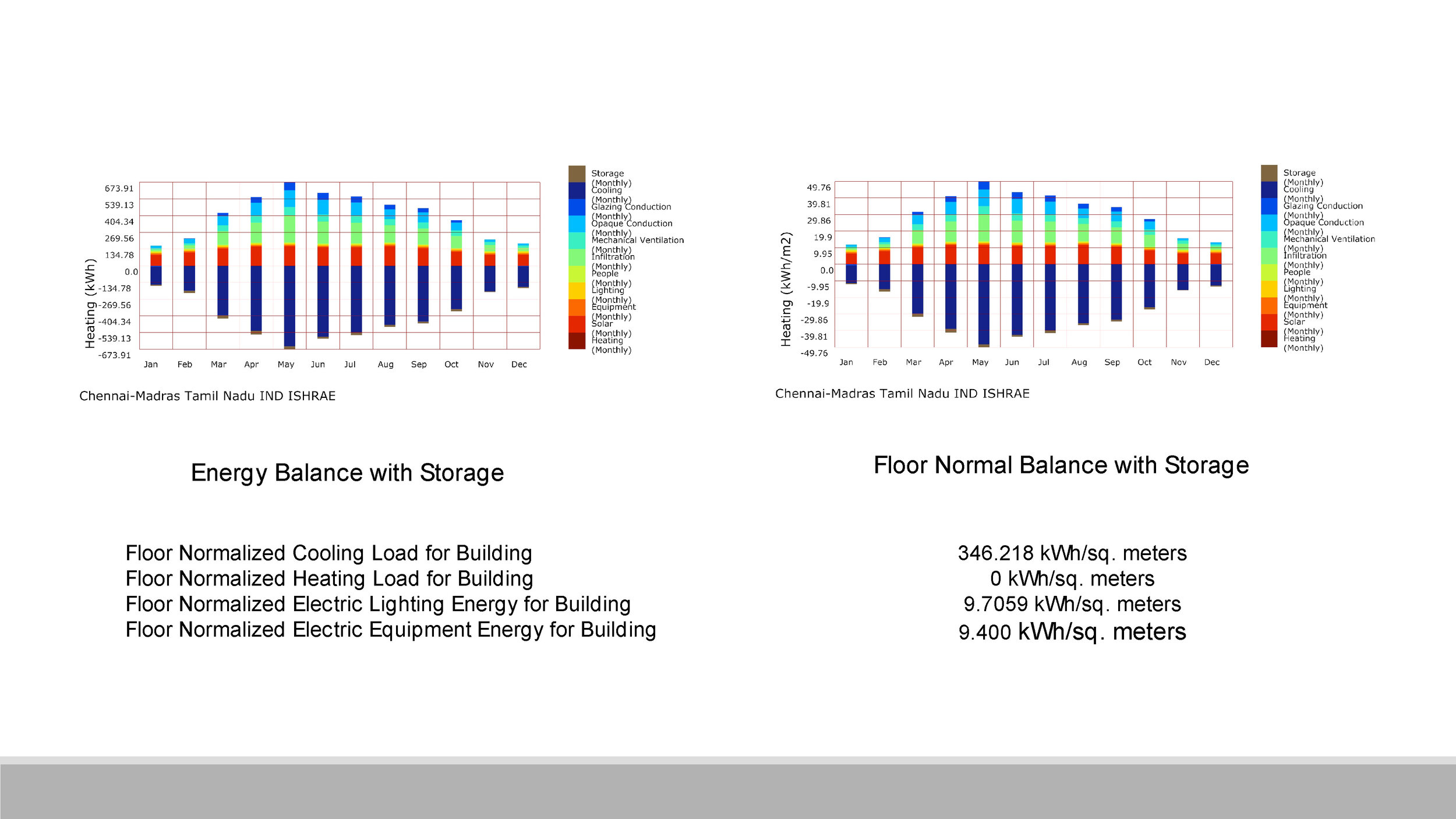
ENERGY
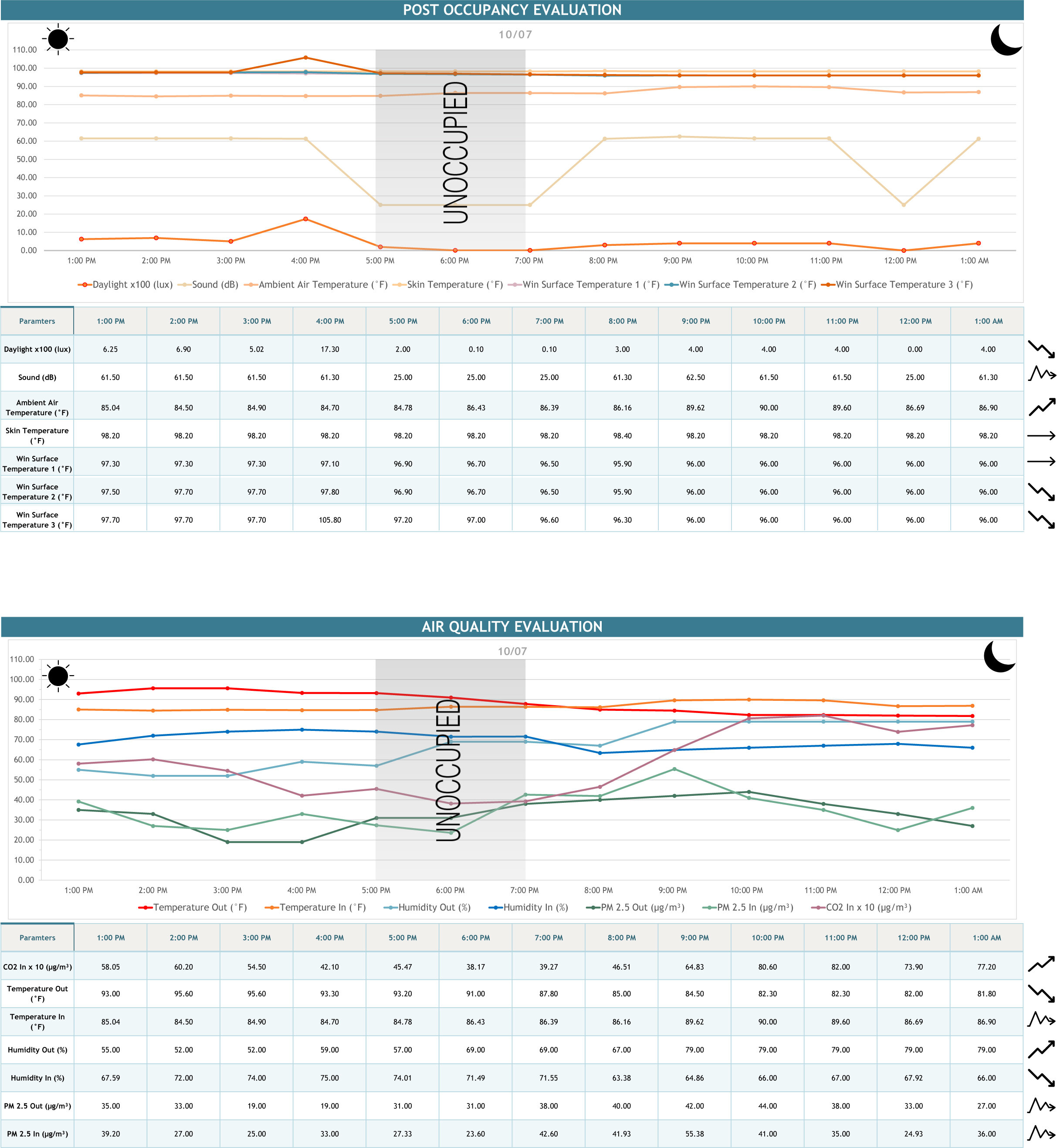
POST-OCCUPANCY TEST
OBSERVATIONS
WHEN WINDOW IS OPENED
•Reduced PM 2.5 levels.
•C02 is nearly the same.
•View clarity is higher.
•There is glare at noon.
•Reduced electrical lighting.
•Reduced dry bulb temperature due to cross - ventilation.
•Direct solar heat gain.
•Decrease in window and wall surface temperature.
•Decrease in humidity due to cross-ventilation.
WHEN WINDOW IS CLOSED
•Reduced productivity.
•Increases C02 level drastically.
•View Quality and Clarity is low.
•Daylight is restricted and highly diffused.
•Additional electrical lighting is utilized to sufficiently light up the room.
•Increases interior dry bulb temperature.
•Increase in window and wall surface temperature.
•Increase in humidity due to infiltration.